Implementing a software package solution can be defined as a collection of “processes”. Each area of activity within implementation is detailed as a process.
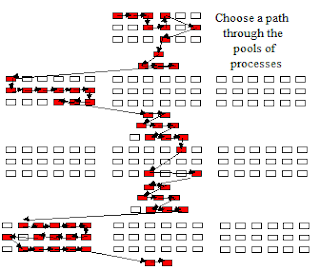
Processes may be mandatory, normal or optional. Alternative processes may sometimes be defined for the same aspect of a project where there are differing needs and market conditions to address. In many cases there will be alternative processes depending on the circumstances of the customer or the scope of the business requirements. In this way a project can be left open so that many different valid paths can be defined through the processes.
Where a new need is identified, new or revised processes can be added into the framework without disturbing the overall design of the project. This allows the implementation to be extensible simply and rapidly to meet all needs in the ever-changing marketplace.
For each process there is detailed documentation including:
- its definition,
- a summary of its purpose and content,
- planning information concerning when it should be used and how it relates to other processes,
- details of deliverables, receivables, tools and materials
- detail of the issues and approach.
This detail may be coupled to an example sub-plan for the process. This is known as a “Process Plan” or “mini-plan”.
Processes available
Processes descriptions are numbered for ease of access. Note that these numbers do not necessarily represent the sequence in which they are performed. Also note that for ease of access the numbers are prefixed by a letter showing the type of segment or path that it applies to. These prefixes are:
L
|
Launch (Project Launch & Segment Launch)
|
R
|
Requirements
|
S
|
Selection
|
D
|
Delivery
|
P
|
Post-implementation (Post-implementation Management, Post‑implementation review, Business Benefits Assessment)
|
Q
|
Quality Audit reviews
|
T
|
Terminate Project
|
Further explanations and detail concerning a Process are detailed in a description and discussed later in the Blog. This will explain the detail of the issues and tasks involved and give some indication concerning the scheduling and planning of the process’s tasks. The Process description also shows some of the main tools and materials that may be used during the Process (see sample process overview table below).
Ref
|
Process
|
Optionality
|
Definition
|
Path Templates
| |||
D010
|
Preliminary Assessment
|
Optional - used where insufficient information is available to plan the project at a detailed level
|
An initial fact-finding study to establish in detail the scope of the project, work required, resource requirements, resource availability, timescale requirements, priorities etc.
|
Segment Launch - Delivery
| |||
D090
|
Implement communications programme
|
Optional - good practice where the success of the project requires the dissemination of information or the promotion of changed attitudes amongst a large number of staff.
|
Undertake the communications activities per plan.
|
Readiness & Roll-out
| |||

No comments :
Post a Comment