An accelerated form of delivery relying
upon a simple approach. This can be
appropriate where there is a small scope, a non-adversarial organisational
environment, and relatively straightforward technical options. Typical criteria for adopting this approach
might be:
- the scope of the project should be small (eg one business area, one business line),
- a small group of empowered people are available within the organisation who can make the decisions in the project,
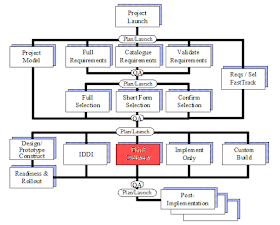
- there is strong pressure to meet deadlines that could not be met with a full approach as in Delivery - IDDI (Integrated Design Development and Implementation)
In many cases, the same processes are
involved, but they are conducted in a simpler way. For example, Brief Implementation Papers are
used in place of Implementation Papers - these require substantially less
evidence of detailed evaluation and consultation. The availability of empowered managers to
agree and sign off designs and activities generally leads to rapid progression
through the processes.
|
Ref
|
Process
|
Optionality
|
Definition
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D200
|
Agree reviewers and sign-off authority
/ responsibility
|
Normal practice
|
Agree a small, empowered group of
authorisers and sign off responsibilities.
|
|
D110
|
Review technical environment and plan
installation
|
Optional - usually required when
insufficient detail was included in the Delivery Approach documentation and
segment plan
|
Plan in detail the physical
installation of the packaged software, additional systems software, hardware,
communications equipment, servers, PCs etc. Note that increasingly this task
is performed by the vendor.
|
|
D120
|
Plan, prepare and conduct project team
training
|
Optional - usually required unless
whole team have requisite experience in all aspects of the solution.
|
Normally, team members need training
before productive work can commence.
Training may also be appropriate for management and other staff
working with the project team.
|
|
D130
|
Install hardware, communications
equipment, system software, and applications software as required for
development, implementation and live running.
|
Optional - required when insufficient
provision is already available for the project.
|
Install and commission items required
for design, development, implementation and live running. This includes system environment
requirements, eg log ons, access security, accounts, budgets etc. With medium systems this is often performed
by the vendor.
|
|
D240
|
Impose issues control and change
control
|
Optional - normal practice where there
are several key users and/or several people on the team. (When no formal mechanism is in use - all
changes must still be documented and agreed in writing.)
|
Issues Control and Change Control
procedures must be in place and used.
Changes from the defined requirements, must be agreed before becoming
firm in the design.
|
|
D150
|
Define and instigate Project Team
responsibilities and techniques for technical support, bug reporting, fixing,
supplier liaison etc.
|
Optional - normal practice where there
are several people in the team and the vendor is not represented.
|
During development there is a need for
clear responsibilities to be defined for running and supporting the
development system. For example, who
applies bug fixes? Who runs the batch jobs?
Who sets up the security access rights?
|
|
D160
|
Consider, review and plan approach to
interfacing and systems integration
|
Optional - used where there will be
significant interfacing or integration.
|
his process looks at the issues which
arise out of the desired levels of integration between separate elements of
the overall project and with external systems. Plans and approaches will be modified
accordingly.
|
|
D180
|
Data conversion strategy
|
Optional - used where existing data
will be brought into the new system
|
A study should be made into the needs
for data conversion. Data availability
and integrity is often wrongly assumed during design work. Recommendations will be made for securing
data as required.
|
|
D300
|
Prepare discussion papers
|
Optional - discussion papers may have
been identified in the segment plan or may be used to explore any particular
issue that arises as the team see fit.
|
These are short papers covering a
particular subject. They are not
formally controlled, reviewed or signed off. Their purpose is to assist in the process of
deciding an issue during the design work.
|
|
D450
|
Design/Prototype - Brief Implementation
Papers
|
Normal practice
|
Design or define each topic within the
project, using prototyping techniques wherever appropriate, documenting the recommended approach and
details in a Brief Implementation Paper (BIP) per topic.
|
|
D600
|
Create detailed specifications for IT development work
|
Optional - used where IT development tasks are involved in the overall technical solution
|
Define the technical requirements to a
sufficient level that they can be used in the detailed design, programming
and construction of a component.
|
|
D650
|
Instigate parallel tasks
|
Optional - used where tasks are required in the overall technical solution
|
Tasks should be
instigated as appropriate. Controls
may be set in place to monitor progress, to ensure adequate quality and to
ensure delivery will be on time and within budget.
|
|
D700
|
Set up system parameters, codes,
structures, etc
|
Normal Practice
|
Each aspect of the system’s basic
configuration system should be set up in accordance with the agreed
implementation papers. Most basic
parameters will have been set during the prototyping. At this stage the full tables are
populated.
|
|
D710
|
Set up screens, queries & reports
etc
|
Optional - as required
|
Each agreed optional customisation of
the system should be set up in accordance with the agreed implementation
papers. Many will have been set during
the prototyping. At this stage the
full tables are populated.
|
|
D720
|
Prepare and instigate operators’
instructions, procedures and manual
|
Optional - depending on suitability of
vendor’s standard materials available
|
Prepare detailed instructions for
the technical operation of the system,
including routine and abnormal running, eg security, disaster recovery. This will normally include
operational-standard JCL and the definition of human/machine interactions.
|
|
D750
|
Prepare and instigate User Procedures
and User Manual / electronic information
|
Normal practice
|
Human procedures should be defined and
agreed as part of the functional design work. Manuals or electronic
documentation of the procedures and how to use the system should be extracted
from the implementation papers and expanded/supplemented as necessary.
|
|
D760
|
Plan, prepare and conduct user and
management training and education
|
Optional - used where user and/or
management training is required
|
Full user training is vital both to the
successful use of the system and also to its acceptance and successful take
up. An effective programme should be
developed based on the identified training needs of all users and management.
|
|
D800
|
Plan, prepare and conduct User / System
/ Acceptance and Integration testing
|
Mandatory
|
Formal testing must be performed to
ensure that all significant aspects of the system are acceptable. Careful planning and preparation is
required to ensure it is complete and comprehensive. Results must be reviewed and signed off by
responsible users.
|
|
D810
|
Plan, prepare and conduct technical
tuning and volume testing
|
Normal practice
|
The system will need technical tuning
to ensure acceptable performance.
Volume testing ensures that full volumes of data and transactions can
be accommodated. Testing should prove
that normal loads can be sustained and peak loads can be accommodated.
|
|
D830
|
Define, plan and agree handover /
cutover
|
Normal practice
|
An analysis should be made of the
logistical requirements for changing over to the new systems. Detailed timings must be considered and
agreed.
|
|
D860
|
Define live support mechanisms
|
Normal practice
|
Dictate responsibilities for support of
the live system and liaison points with the vendor.
|
|
D880
|
Load start up data
|
Normal practice
|
All initial data should be loaded. Includes running of conversion suites and
manual data entry.
|
|
D890
|
Validate start up data
|
Normal practice
|
Complete loaded data should be
validated and signed off by the responsible user managers.
|
|
D900
|
Decision to go live
|
Mandatory
|
The ultimate governing body or manager
for the project should take the definitive decision to go live. It must be certain that all vital
pre-conditions have been satisfied to at least a minimum level, eg testing,
data validation, training, organisation.
|

No comments:
Post a Comment